Selecting Optimal DIN Rail Power Supplies
Standardized DIN rails make it easy to fit a power supply in an electrical enclosure. However, designers can't afford to overlook the efficiency and heat dissipation issues that can impact the reliability, service lifetime, and operational cost of an application.
Unreliable power supplies can be infuriating to system designers and their customers. It is time-consuming and costly to replace a power unit earlier than anticipated, and system downtime is simply unacceptable in many applications.
Heat goes hand in hand with inefficiency and failures in DIN power supplies. Heat can dry out the electrolytic capacitors used in power supplies that store electricity and smooth fluctuations in voltage and current.
Capacitors are the most temperature-sensitive components and are often the first to fail in power supplies. A temperature rise of 10°C can halve their expected service life, so protecting against overheating is a critical design consideration. Semiconductors and solder joints are also vulnerable to temperature increases.
By employing efficient design, proper thermal management, and selecting high-quality components, product designers can mitigate the effects of heat, prolong service life, and enhance system reliability.
Optimizing high-efficiency designs
Efficiency in a DIN rail power supply is represented by a ratio of output power to input power. A power supply that operates at 95% efficiency, for example, loses only 5% of the input energy as heat, while a less efficient supply at 85% loses 15%.
By reducing heat generation, highly efficient power supplies decrease cooling requirements, better ensure that electrolytic capacitors attain the service lifetime specified by a manufacturer, and enhance the overall reliability of the power supply unit.
Optimized thermal management practices can be used to dissipate heat into the external environment to lower internal temperatures. In addition, power supplies can minimize heat exposure of temperature-sensitive components to enhance overall durability and service life.
Power supplies are becoming increasingly complex and simultaneously shrinking in size. Limited space inside them underscores the crucial role of installing cooling ducts, which designers would be well-served to view as integral components. Sophisticated cooling concepts may often eliminate the requirement for internal heat sinks, which further reduces a power supply’s weight and can significantly reduce production costs.
Power unit manufacturing practices
Manufacturers like PULS demonstrate that it is possible to design power supplies that are both reliable and environmentally friendly through high efficiency, optimized thermal management, and precise measurement techniques.
Measuring power supply efficiency is complex. System developers should evaluate manufacturer-provided data to ensure it is obtained through standardized testing procedures. This ensures metrics are trustworthy and comparable across different products and vendors. Efficiency should be measured under conditions that closely mimic actual system loads, including variable loads and temperature ranges.
Component placement is also important. Strategically positioning life-determining components in cooler areas can be instrumental in maximizing service life. Electrolytic capacitors, for example, can benefit from placement near cool air flow (Figure 1).
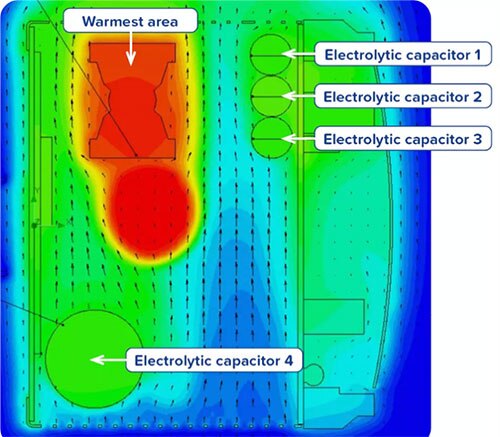 Figure 1: A heat map demonstrates the advantage of locating electrolytic capacitors near the cooling air flow and away from hot spots. (Image source: PULS)
Figure 1: A heat map demonstrates the advantage of locating electrolytic capacitors near the cooling air flow and away from hot spots. (Image source: PULS)
PULS provides a comprehensive range of DIN power supplies. Its 240 W CP10 series products achieve efficiencies up to 95.2%, and the 480 W CP20 series units reach efficiencies as high as 95.6%. The high efficiency and advanced thermal design of both series minimizes internal heat and makes them well-suited for demanding industrial applications.
The company tested its DIMENSION CP10.241 power supply (Figure 2) in an enclosure and loaded it at 80% of its rated power. According to those tests, the temperature in the enclosure increased by approximately 19°C after four hours of operation. A device with 6.7% lower efficiency would increase the temperature in the control cabinet to 35.3°C. The 16.3°C temperature increase would cut the service lifetime of the electrolytic capacitors by more than half.
 Figure 2: The PULS DIMENSION CP10.241. (Image source: PULS)
Figure 2: The PULS DIMENSION CP10.241. (Image source: PULS)
Product designers should also evaluate how efficiently a power supply performs when not operating at full capacity, as partial load efficiencies are increasingly important in designing practical and cost-effective applications. High full-load efficiencies make it possible to utilize small designs, but relatively few power supplies are required to operate at full load. PULS testing of its DIMENSION CP20.241 demonstrates how efficiencies can be impacted across different loads (Figure 3).
 Figure 3: How the PULS DIMENSION CP20.241 efficiency is impacted across different loads. (Image source: PULS)
Figure 3: How the PULS DIMENSION CP20.241 efficiency is impacted across different loads. (Image source: PULS)
Product designers should also ensure they are selecting power supplies that are compliant with energy efficiency standards such as Energy Star and IEC 62368-1, as well as Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) and the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) directives addressing hazardous materials and electronic waste management.
Conclusion
Efficiency and heat dissipation in DIN rail power supplies are critical considerations for product designers. High efficiency reduces operational costs, minimizes environmental impact, and improves system reliability. Effective heat dissipation strategies ensure component longevity and prevent system failures. The PULS DIMENSION portfolio includes a wide range of DIN rail power supplies to provide suitable solutions for almost any application.

Have questions or comments? Continue the conversation on TechForum, DigiKey's online community and technical resource.
Visit TechForum









