How to Specify Cables to Ensure Success in Extreme Environments
Contributed By DigiKey's North American Editors
2025-06-27
Arctic pipeline controls, mass transit systems, mining and military equipment, and food, beverage, and petrochemical operations are examples of applications that operate in extreme environments and require robust cabling to ensure uninterrupted operation and safety. A key requirement is extended temperature operation from -50°C to +125°C.
The cables should have thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) insulation that delivers three times the low-temperature flexibility of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), is solvent- and water-resistant, has excellent ultraviolet (UV) light stability, and is recyclable for improved sustainability. They should be suitable for use in harsh outdoor conditions, exposed to the elements, or for direct burial to expedite installation.
They must meet strict UL and CSA requirements and be available in multipair and multiconductor configurations with a choice of tray cable (TC), power limited tray cable (PLTC), or wind turbine tray cable (WTTC) performance, a range of electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding options, and voltage ratings to suit a variety of application scenarios.
This article reviews the performance and sustainability benefits of using TPE insulation with a focus on the construction of Xtra-Guard 4 cables from Alpha Wire. It examines how those cables simplify installation in challenging locations and concludes by briefly considering how heat shrink tubing such as FIT-600, which meets AMS-DTL-23053/1 Class 1 and 2 standards, can enhance installations using Xtra-Guard 4 cables.
PVC limitations & TPE solutions
PVC is a widely used and highly capable insulation material, but it’s not a panacea. In certain classes of applications, like cables for extreme environments, it may not be the best option. In those applications, there’s an alternative called TPE that can be useful.
TPE addresses performance and environmental concerns associated with PVC. In applications like arctic pipeline and renewable energy system controls, mass transit systems, and mining and military equipment that can experience extremely low temperatures, TPE can be a better choice.
TPEs are primarily a combination of a hard thermoplastic polymer and a soft, elastomeric polymer blended or copolymerized to create the optimal performance for specific applications. The TPE used on Alpha Wire’s Xtra-Guard Flex 4 cables is 3x more flexible than PVC at low temperatures. That simplifies installation and maintenance.
Some applications experience extremely high temperatures, such as sanitation washdowns in food and beverage processing and specific petrochemical processes. Rated for use up to +125°C, TPE is an excellent choice, delivering consistent reliability at elevated temperatures. It also withstands hazards such as solvents, water, oil, UV rays from the sun, and flames, which are found in a wide range of applications, better than PVC alternatives.
Ultimately, every system has a finite life cycle, and in the end, recycling and sustainability are crucial factors in determining the longer-term impact of the installation. This is another area where TPE excels. The halogens (like chlorine, fluoride, and bromine) are highly reactive. Typical PVC contains about 29% chlorine by weight. Other alternatives, such as fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP) and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE, often referred to as Teflon), can contain up to 76% fluorine.
During normal use, materials like PVC, FEP, and PTFE are benign and highly useful. At the end of life, when recycled, they can be sources of hazardous and toxic compounds. TPE is a thermoplastic, meaning it can be repeatedly melted and reshaped without degrading. Using TPE insulation helps reduce waste, conserve resources, and minimizes the environmental impact associated with end-of-life disposal.
Optimized shielding
EMI can pose another environmental hazard for electronic systems, and Alpha Wire’s Xtra-Guard 4 cables provide designers with three shielding options for addressing low, medium, and high levels of EMI (Figure 1).
- In low EMI environments, unshielded cables are suitable and deliver the smallest diameter and lowest weight solution.
- In moderate EMI situations, aluminum/polyester foil shielding can be adequate. Foil shields offer an intermediate solution in terms of EMI performance, cable size, and weight. The tinned copper drain wire simplifies grounding the cable, thereby improving shielding effectiveness.
- When dealing with high EMI levels, designers can turn to Alpha’s Supra-Shield cables that combine an aluminum/polyester/aluminum foil and a tinned copper braid shield with tight 75% coverage. Supra-Shield provides high-performance shielding across the entire frequency spectrum, ensuring system integrity while maintaining cable flexibility for easy installation.
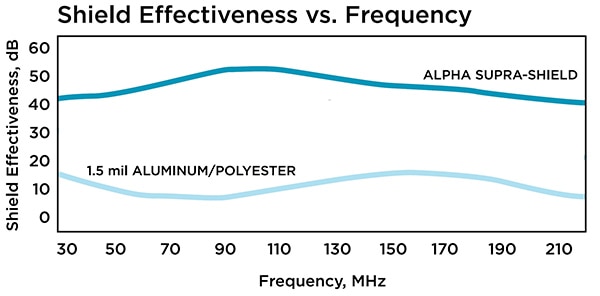 Figure 1: Applications that require maximum EMI shield effectiveness can turn to Supra-Shield, which delivers better performance across the frequency range compared with conventional aluminum/polyester foil shielding. (Image Source: Alpha Wire)
Figure 1: Applications that require maximum EMI shield effectiveness can turn to Supra-Shield, which delivers better performance across the frequency range compared with conventional aluminum/polyester foil shielding. (Image Source: Alpha Wire)
More cable construction options
Insulation materials and shielding are only two aspects of cable construction. There are also the conductors that form the heart of the assembly, facilitating the flow of electrical energy and information for system operation.
Xtra-Guard 4 cables are offered with a choice of multiconductor and multipair designs. Both types have multiple wires in a single jacket, but they differ in their structure and intended applications.
Multiple individual conductors are bundled together to form a multiconductor cable. They are suited for general-purpose applications, such as power distribution or simple control wiring when signal integrity is not a design concern.
In multipair cables, the pairs of conductors are twisted together before being integrated into the cable. Twisting reduces noise and interference, making each pair suitable for higher-speed data transmission and communication applications (Figure 2).
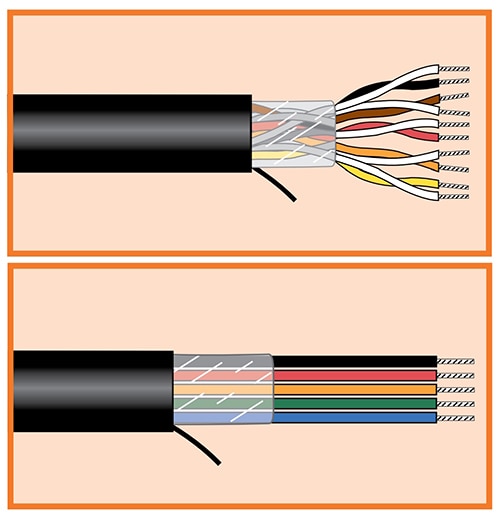 Figure 2: Xtra-Guard 4 cables are available with multiple twisted wire pairs (top) and multiple individual conductors (bottom). (Image Source: Alpha Wire)
Figure 2: Xtra-Guard 4 cables are available with multiple twisted wire pairs (top) and multiple individual conductors (bottom). (Image Source: Alpha Wire)
Multiconductor cables are available with conductors from 16 to 24 AWG, 2 to 40 conductors, and various stranding structures, including 16/30, 7/28, and 41/30. Multipair cables are available with conductors ranging from 18 to 24 AWG, 1 to 19 pairs, and with stranding options of 16/30, 7/28, 7/30, and 7/32.
Cable ratings
Additional pieces of the puzzle when specifying cables to ensure success in extreme environments are the voltage rating and UL type. Multiconductor Xtra-Guard 4 cables are available, rated at 300 V and 600 V. Multipair designs are available for 300 V, which are suited for data transmission and communication applications.
Cable trays are often used as an alternative to conduit or open wiring. They support efficient cable installation, management, and maintenance. There are two primary types of UL-rated cable tray cables. The main difference is their voltage ratings.
Type TC is rated 600 V, making them suitable for power and control circuits in industrial applications. Type PLTC cables are rated at 300 V and are used primarily for signal and communications circuits. Xtra-Guard 4 multiconductor cables are available for both TC and PLTC applications, while multipair cables are available for PLTC applications (except 24 AWG).
TC-rated cables are often used in applications where flame retardance is desired. PLTC cables can be used in Class 2 and Class 3 circuits, as defined by the National Electrical Code (NEC).
Class 2 circuits have a minimum voltage rating of 150 V, while Class 3 circuits require a minimum rating of 300 V. Both are limited to a maximum power of 100 VA and are safe from fire initiation. Class 2 circuits are considered shock-safe due to their low voltage and power limits, while Class 3 circuits often require additional safeguards for shock protection.
Xtra-Guard 4 cables are also UL WTTC-rated for use in wind turbine applications, and they are approved by the Pennsylvania Bureau of Deep Mining Safety for mine-wide monitoring systems (except 14 AWG). Alpha Wire offers a comprehensive line of Xtra-Guard 4 cables (Figure 3). A few examples include:
- 45053, multi-conductor unshielded, with 3 20 AWG 7/28 conductors, rated for 300 V
- 45440/9, multi-conductor foil shielded, with 9 16 AWG 19/.0117 conductors, rated for 600 V
- 45162 multi-conductor Supra Shielded, with 2 18 AWG 16/30 conductors, rated for 300 V
- 45032 multi-pair unshielded, with 2 18 AWG 16/30 conductor pairs, rated for 300 V
- 45484 multi-pair foil-shielded, with 4 22 AWG 7/30 conductor pairs, rated for 300 V
- 45126 multi-pair Supra-Shielded, with 6 22 AWG 7/30 conductor pairs rated for 300 V
 Figure 3: Xtra-Guard 4 cables are available in a variety of cable and shielding configurations and with ratings of 300 V and 600 V. (Image Source: Alpha Wire)
Figure 3: Xtra-Guard 4 cables are available in a variety of cable and shielding configurations and with ratings of 300 V and 600 V. (Image Source: Alpha Wire)
Easy & robust installation
After the cable has been specified and matched to the application, the final puzzle piece is easy and robust installation. In addition to the cable tray installations detailed above, designers can use Xtra-Guard 4 cables in outdoor and direct burial applications, where they combat the impact of weathering and UV aging without requiring a conduit. That can dramatically simplify and speed up installation.
These cables include a nylon rip cord for easy jacket stripping. Alpha Wire’s FIT heat shrink tubing can provide a reliable way to protect and seal terminations, as well as add additional mechanical ruggedness.
FIT 600 heat shrink tubing is a popular choice. For example, model F6001IN BK005 is 1” in diameter before shrinking and made with chlorinated polyolefin (CPO). CPO provides a balance of flexibility with heat and chemical resistance. It maintains flexibility at low temperatures and is more flexible than standard cross-linked polyolefin (XLPO) heat shrink tubing. CPO also offers twice the tensile strength of silicone rubber heat shrink tubing with an operating temperature range of -75°C to +121°C and pairs well with Xtra-Guard 4 cables in extreme environments (Figure 4).
 Figure 4: Alpha Wire’s FIT 600 heat shrink tubing matches well with the performance of Xtra-Guard 4 cables in extreme environments. (Image Source: Alpha Wire)
Figure 4: Alpha Wire’s FIT 600 heat shrink tubing matches well with the performance of Xtra-Guard 4 cables in extreme environments. (Image Source: Alpha Wire)
The FIT 600 heat shrink tubing series also complies with AMS-DTL-23053/1 Class 1 and 2. AMS-DTL-23053/1 is a military specification for heat shrink tubing used for electrical insulation, strain relief, and abrasion protection in military and aerospace systems.
The standard specifies both Class 1, which is heavier wall tubing, and Class 2, which is medium wall tubing. The nominal recovered wall thickness is directly related to the expanded size of the tubing before shrinking. For example, for a 1" nominal size before shrinking, the recovered wall thickness for medium wall tubing is about 0.070 inches (1.78 mm).
Conclusion
Alpha Wire Xtra-Guard 4 cables have what it takes to ensure success in extreme environments. Being specified for temperatures from -50°C to +125°C, they are suitable for use in cold environments in Arctic pipeline controls, in extreme heat in petrochemical plants, and they can withstand steam cleaning and sterilization in food and beverage processing operations.
Their TPE insulation provides superior flexibility as well as resistance to water, solvents, UV rays, and other environmental challenges. They are available in a variety of conductor configurations, EMI shielding levels, and voltage ratings to meet the requirements of a wide array of applications.
They are UL-approved for various Tray Cable installation types or direct burial. Finally, the FIT 600 heat shrink tubing provides a good match for the flexibility, chemical resistance, and operating temperature capabilities of Xtra-Guard 4 cables. Xtra-Guard 4 is available in 100’ and 1000’ spools exclusively from DigiKey.
Recommended reading:
- Subtle Considerations for Connectors in Harsh and Extreme Environments
- Select the Right Connector to Ensure High-Current Power Integrity in Extreme Environments
- The Surprising Innovations Steel Cable Ties Hold for Harsh Environments
- Considerations for Custom Rugged Connector Solutions
- Specifying and Using VFD Cables to Improve Reliability and Safety and Reduce Carbon Emissions

Disclaimer: The opinions, beliefs, and viewpoints expressed by the various authors and/or forum participants on this website do not necessarily reflect the opinions, beliefs, and viewpoints of DigiKey or official policies of DigiKey.









