Understanding Capacitors: Basics, Types, and Where They Shine
2025-08-06 | By Nadir James
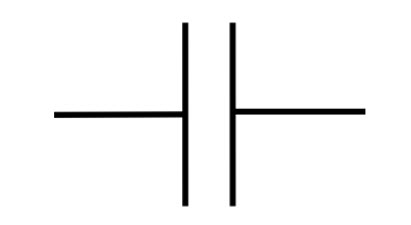
What is a Capacitor?
At its core, a capacitor is an electronic component that stores and releases electrical energy. It consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material known as a dielectric. When voltage is applied across the plates, an electric field develops, storing energy for future use.
How Do Capacitors Work?
When a voltage is applied across the terminals, electrons accumulate on one plate, creating a negative charge, while the opposite plate loses electrons and becomes positively charged. This difference in charge creates a potential energy-or electric field-across the dielectric. Once the power source is removed, the capacitor can discharge, releasing the stored energy back into the circuit.
Types of Capacitors (With Advantages & Common Use Cases)
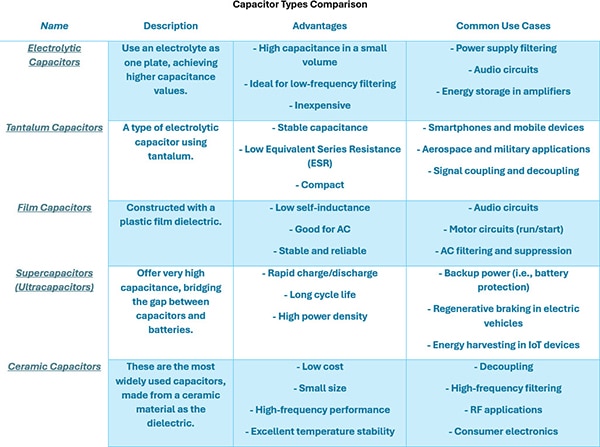
Supercapacitors (Ultracapacitors)
Key Takeaways
Capacitors are vital for timing, filtering, and storing energy. Each type has strengths suited to specific applications.
Final Thoughts
Capacitors are important electronic components that store/release energy, which helps to stabilize voltage, filter signals, and manage power in circuits. Each type - ceramic, electrolytic, tantalum, supercapacitor, and film each has distinct advantages for specific applications, from high-frequency filtering to energy storage. Different factors like capacitance, size, frequency response, polarity, and durability play key roles in selecting the right capacitor. The ceramic and film capacitors excel in stability and high-frequency use, while the electrolytic and tantalum types offer higher capacitance for compact spaces. Lastly, supercapacitors bridge the gap between batteries/capacitors, helping rapid charge/discharge in modern energy systems. Understanding these different characteristics ensures optimal performance and reliability across a wide range of electronic devices.