TDK CeraCharge™ Rechargeable Battery – A New Technology for IoT Applications
If you have ever encountered any of the challenges or issues listed below, then you might be interested in reading this blog:
- Air shipping restrictions due to IATA regulations for the products containing Li-ion batteries
- Safety issues with Li-ion batteries
- Manufacturing challenges in the automatic assembly process of coin batteries
- Robustness of a product populated with the coin battery or battery holder
- The final product is used in space
- A need of wide operating temperature range
- A need to get rid of a coin battery or supercapacitor
The answer for all of the above wonderings is TDK CeraCharge™ – currently the world’s smallest, rechargeable, easy-to-assemble, solid-state multilayer ceramic battery that possesses the following unique features:
- All ceramic structure
- does not leak
- does not burn
- does not explode
- SMT technology
- reflow solderable
- no need to change battery
- mounted on PCB, no need for battery holders
- high volume manufacturing
- Product robustness
- wide temperature range
- suitable for vacuum applications
TDK CeraCharge combines the advantages of Li-ion batteries with the safety and manufacturing benefits of ceramic multilayer components as shown in Figure 1.
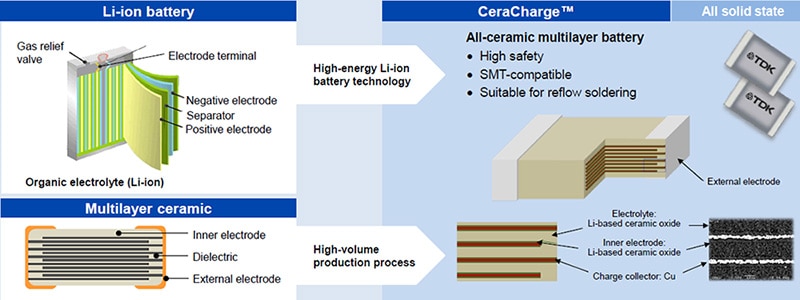 Figure 1: CeraCharge structure (Image source: TDK)
Figure 1: CeraCharge structure (Image source: TDK)
TDK CeraCharge features fast and pulsed discharging as shown in Figure 2.
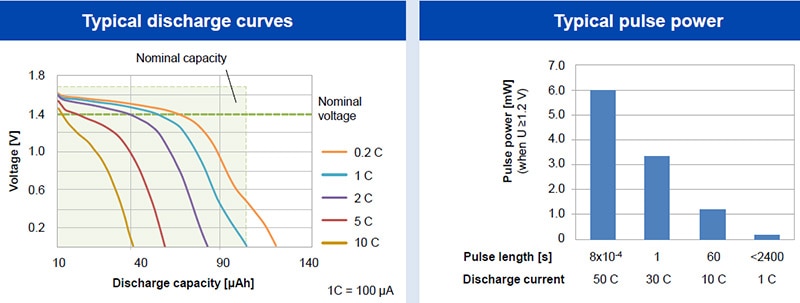 Figure 2: CeraCharge typical discharge curves and pulse power. (Image source: TDK)
Figure 2: CeraCharge typical discharge curves and pulse power. (Image source: TDK)
Table 1 summarizes the basic characteristics of the CeraCharge battery.
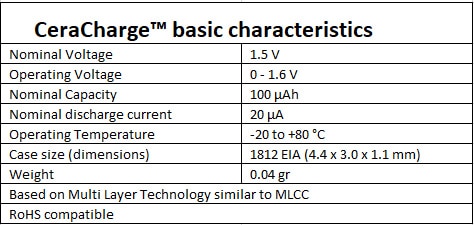 Table 1: CeraCharge basic characteristics
Table 1: CeraCharge basic characteristics
TDK CeraCharge can be connected in both series and parallel for maximum design flexibility as shown in Figure 3. When connected in parallel, the discharging capacity is multiplied by the number of the connected CeraCharge batteries. When connected in series, the output voltage is multiplied by the number of the connected CeraCharge batteries.
 Figure 3: Serial and parallel connection of CeraCharge batteries (Image source: TDK)
Figure 3: Serial and parallel connection of CeraCharge batteries (Image source: TDK)
The main application areas for CeraCharge include (but are not limited to):
1.) Wearable IoT devices as shown in Figure 4
 Figure 4: CeraCharge wearable IoT devices application block diagram (Image source: TDK)
Figure 4: CeraCharge wearable IoT devices application block diagram (Image source: TDK)
2.) Real-time clocks (RTCs) as shown in Figure 5
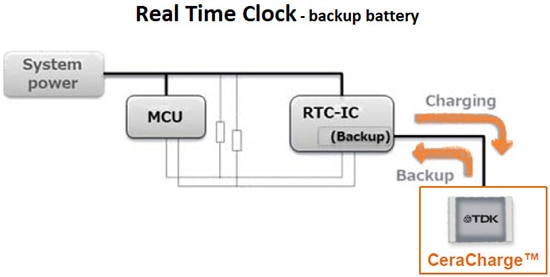 Figure 5: CeraCharge RTC backup battery application block diagram (Image source: TDK)
Figure 5: CeraCharge RTC backup battery application block diagram (Image source: TDK)
3.) Energy harvesting as shown in Figure 6
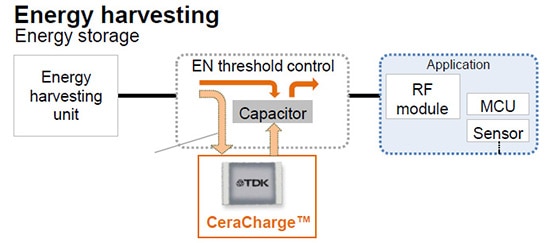 Figure 6: CeraCharge energy harvesting application block diagram (Image source: TDK)
Figure 6: CeraCharge energy harvesting application block diagram (Image source: TDK)
4.) Bluetooth Low-Energy (BLE) beacons as shown in Figure 7
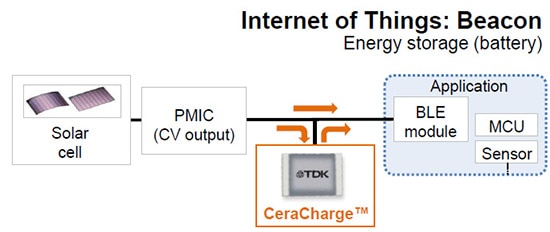 Figure 7: CeraCharge BLE beacons application block diagram (Image source: TDK)
Figure 7: CeraCharge BLE beacons application block diagram (Image source: TDK)
More detailed technical information on TDK CeraCharge technology, area of usage, application examples, charging sequence, mounting process, and more can be found in the CeraCharge Data sheet and the CeraCharge Application Note v1.
Editorial Note: This part is an engineering sample and is not fully tested. This part should only be used for functional evaluation and proof of concept, not for production or end use.

Have questions or comments? Continue the conversation on TechForum, DigiKey's online community and technical resource.
Visit TechForum