Simplify Implementation of Single-Pair Ethernet Networking for Critical Time-Sensitive Applications
Contributed By DigiKey's North American Editors
2025-08-20
High-speed real-time Ethernet communication is increasingly vital for time-sensitive applications in industrial automation and automotive systems. In addressing requirements for these types of applications, conventional multipair Ethernet often falls short due to its nondeterministic performance, bulky cable harnesses, and elevated power consumption.
More effective solutions rely on single-pair Ethernet (SPE) standards, which offer a streamlined physical layer (PHY) but can present performance challenges for extended cable reach and functional safety readiness, as well as implementation challenges related to the availability of effective design resources. Engineers need a comprehensive solution that meets stringent performance requirements for real-time SPE networking while speeding their implementation.
This article outlines the networking requirements and related issues facing designers of critical, time-sensitive applications, particularly in the industrial and automotive sectors. It then introduces SPE solutions from Microchip Technology, including an Ethernet PHY transceiver, evaluation boards, and associated design resources that help designers meet the emerging challenges in implementing standards-compliant SPE networking systems.
How critical application requirements drive demand for real-time Ethernet
Real-time Ethernet plays a growing role across many critical industrial and automotive applications. In the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and industrial control systems, high-precision coordination among sensors, controllers, and actuators requires deterministic communication networks enabled by protocols such as IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol (PTP). In automotive applications, including advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), infotainment, and telematics subsystems, reliable real-time data exchange needs to withstand the extreme conditions of the vehicular environment.
Whether on the factory floor or inside a vehicle, time-sensitive networks must guarantee low and bounded latency, high fault tolerance, and minimal jitter. The ability to maintain synchronization across devices is essential, particularly in environments where millisecond response times are critical for system operation and safety. At the same time, networking solutions must accommodate the limited space available for network subsystems in manufacturing cells or vehicular chassis.
How to meet networking requirements for time-sensitive, space-constrained applications
Regulated under IEEE 802.3bw (100BASE-T1) and IEEE 802.3bp (1000BASE-T1) standards for gigabit Ethernet (GbE) in industrial and automotive applications, SPE has emerged as a streamlined PHY alternative to conventional Ethernet. SPE supports the rigorous requirements of time-sensitive applications while reducing cable complexity and system cost. However, despite gaining these advantages, SPE-based network designers still face challenges in integrating suitable devices and ensuring their functional safety readiness.
Microchip Technology’s LAN8872 1000BASE-T1 SPE PHY transceiver (Figure 1) and associated design resources support developers in meeting these emerging challenges when implementing standards-compliant SPE networking. The LAN8872 integrates a complete PHY subsystem, including a physical coding sublayer (PCS), a finite-state machine (FSM), an analog front-end (AFE), a low-dropout (LDO) regulator, voltage monitoring, on-chip termination, and integrated filtering.
 Figure 1: The LAN8872 provides an integrated 1000BASE-T1 PHY transceiver, complete with a PCS, an LDO regulator, voltage monitoring, an AFE, an FSM, on-chip termination, and integrated filtering. (Image source: Microchip Technology)
Figure 1: The LAN8872 provides an integrated 1000BASE-T1 PHY transceiver, complete with a PCS, an LDO regulator, voltage monitoring, an AFE, an FSM, on-chip termination, and integrated filtering. (Image source: Microchip Technology)
With built-in support for IEEE 1588-2019 and IEEE 802.1AS-2020 precision clock synchronization protocol standards, the LAN8872 is fully compatible with audio video bridging (AVB) and IEEE 802.1 Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) standards for real-time Ethernet networks. While the LAN8872’s deterministic timing capabilities help developers maintain tight synchronization across multiple systems, its energy management capabilities address the need for robust low-power connectivity even in harsh environments.
Simplifying the design of low-power SPE networks
The LAN8872 incorporates Microchip’s EtherGREEN energy-efficient technology, enabling the device to typically draw only 15 microamperes (μA) in its ultra-low-power sleep mode. Supporting OPEN Alliance Technical Committee 10 (TC10) standard remote sleep and wake-up mechanisms, the device can recognize sleep requests and wake up in response to WAKE_IN pulses. Its INH output allows the device to enable or disable the electronic control unit (ECU) supply. Built into the LAN8872, Microchip’s FlexPWR power management technology delivers further energy savings through variable I/O and core power supply voltages.
The LAN8872’s high level of integration further simplifies design. Along with its extensive integrated functionality, its on-chip termination resistors and integrated transmission filtering combine to enable solutions with a compact footprint and low electromagnetic interference (EMI). For system-level integration, the LAN8872 features a reference clock output and a standard serial gigabit media-independent interface (SGMII), simplifying interfaces with Ethernet media access controllers (MACs) or MAC-capable devices, including systems-on-chip (SoCs), microcontroller units (MCUs), and field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) (Figure 2).
 Figure 2: Developers need only a few additional components to integrate the LAN8872 PHY transceiver in their SPE networking solutions. (Image source: Microchip Technology)
Figure 2: Developers need only a few additional components to integrate the LAN8872 PHY transceiver in their SPE networking solutions. (Image source: Microchip Technology)
Compliant with IEEE 802.3bp-2016, the LAN8872 is designed to deliver gigabit performance over a single pair of wires while supporting troubleshooting in critical industrial and automotive networks. The device aids network diagnostics with features including cable-defect detection of shorts or opens, a receiver signal quality indicator (SQI), over-temperature protection, under-voltage protection, comprehensive status interrupt support, and various loopback and test modes.
Accelerating the design of LAN8872-based SPE solutions
To accelerate design and development, Microchip provides evaluation boards built to meet different developer requirements. To facilitate system-level design test and validation, Microchip’s EV75E52A EVB-LAN8870-MC evaluation board (Figure 3) provides a complete media converter that bridges 1000BASE-T1 and standard gigabit Ethernet. Developers simply connect a CAT5 Ethernet cable from their GbE port to the board’s RJ-45 jack and connect a single twisted-pair cable from their SPE network to the board’s T1 automotive Ethernet connector.
 Figure 3: The EV75E52A EVB-LAN8870-MC evaluation board provides a complete media converter for testing designs connecting SPE networks with gigabit Ethernet. (Image source: Microchip Technology)
Figure 3: The EV75E52A EVB-LAN8870-MC evaluation board provides a complete media converter for testing designs connecting SPE networks with gigabit Ethernet. (Image source: Microchip Technology)
For developers focused on evaluating PHY capabilities, Microchip’s EV39G24A EVB-LAN8870-RGMII board (Figure 4) provides a complete PHY subsystem with a direct PHY interface.
 Figure 4: The EV39G24A EVB-LAN8870-RGMII board provides a complete PHY subsystem for PHY evaluation in SPE designs. (Image source: Microchip Technology)
Figure 4: The EV39G24A EVB-LAN8870-RGMII board provides a complete PHY subsystem for PHY evaluation in SPE designs. (Image source: Microchip Technology)
The EVB-LAN8870-RGMII board (Figure 5, left) is designed to attach through its PHY interface connector to Microchip Ethernet development systems (EDS) boards, including the EV88E76A EVB-LAN7801-EDS and the EVB-LAN7431-EDS (Figure 5, right).
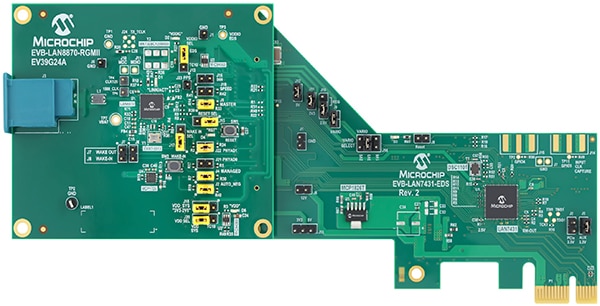
Figure 5: Developers can plug the EVB-LAN8870-RGMII PHY board (left) into EDS boards such as the EVB-LAN7431-EDS (right) to access all PHY registers through development host drivers. (Image source: Microchip Technology)
Developers working with the EVB-LAN8870-RGMII board can access all PHY registers through EDS board drivers running on Windows or Linux hosts. Those working with the EVB-LAN8870-MC can configure and monitor transceiver performance through a Windows-based graphical user interface (GUI) software package.
To help accelerate the development of custom SPE designs, Microchip provides comprehensive reference schematics and configuration guidelines, as well as an extensive software ecosystem to support LAN8872 integration. Drivers are available for popular platforms, including Linux, FreeRTOS, and AUTOSAR. Microchip’s MPLAB Harmony embedded software development framework includes integrated drivers, peripheral libraries, and Code Configurator support that streamlines the configuration and testing of LAN8872 PHY designs.
Beyond these development resources, Microchip’s complimentary MicroCHECK design review service offers direct assistance for each stage of implementation from concept to layout. With the MicroCHECK service, developers can submit their schematics and printed circuit board (pc board) layouts for expert review and receive actionable feedback on signal integrity, power distribution, and compliance with recommended design practices. By using the MicroCHECK service in early design stages, developers can minimize the risk of PHY-related implementation issues arising later in the production process.
In a typical development workflow, developers begin by evaluating PHY capabilities in their design using one of Microchip’s reference boards. After validating PHY performance and behavior in the target environment, they incorporate the PHY into a custom design using reference schematics and layout recommendations. Before committing to a prototype build, they submit their design for MicroCHECK review, ensuring that their implementation is robust and production-ready.
Conclusion
As real-time Ethernet becomes essential in more industrial and automotive applications, developers face growing pressure to implement compact, standards-compliant, low-power networking solutions. Backed by comprehensive resources and expert project review support, Microchip’s LAN8872 1000BASE-T1 PHY helps accelerate the development of designs needed to ensure reliable, high-performance SPE connectivity.

Disclaimer: The opinions, beliefs, and viewpoints expressed by the various authors and/or forum participants on this website do not necessarily reflect the opinions, beliefs, and viewpoints of DigiKey or official policies of DigiKey.








